I2C - Inter-Integrated Circuit
I2C Class in the Reference.
Hardware I2C
On most boards there are hardware I2C peripherals. Check out the
pin diagram on the reference page for your board and look for
pins marked with an I2C tag.
You can use it as follows.
// set up I2C
I2C1.setup({ scl : B6, sda: B7 });
// read 6 bytes from address 0x52
var d = I2C1.readFrom(0x52, 6);
// Write a single byte (0) to address 0x52
I2C1.writeTo(0x52, 0);
See the reference for I2C.setup for more information on the arguments that can be passed in.
Software I2C
If you don't have access to your board's pins, you can also emulate I2C in software:
// set up I2C
var i2c = new I2C();
i2c.setup({ scl : B6, sda: B7 });
// read 6 bytes from address 0x52
var d = i2c.readFrom(0x52, 6);
// Write a single byte (0) to address 0x52
i2c.writeTo(0x52, 0);
See the reference for I2C.setup for more information on the arguments that can be passed in.
Speed (bit rate)
Pretty much all I2C devices are guaranteed to support 100kBits/sec transfer
speed for I2C, so that is the default in Espruino. However you can specify
higher speeds with bitrate in I2C.setup if your
device supports it, eg:
i2c.setup({ scl : B6, sda: B7, bitrate: 400000 });
Using I2C
 INA226 Current/Voltage Measurement IC
INA226 Current/Voltage Measurement IC
 Renesas FS3000 Air velocity sensor module
Renesas FS3000 Air velocity sensor module
 AHT10 RH/TEMP Sensor
AHT10 RH/TEMP Sensor
 BH1792 I2C Heart rate Sensor
BH1792 I2C Heart rate Sensor
 TMP117 Temperature Sensor
TMP117 Temperature Sensor
 MLX90632 non-contact temperature sensor
MLX90632 non-contact temperature sensor
 MAX30102 Heart rate monitor
MAX30102 Heart rate monitor
 HD44780 Character LCD
HD44780 Character LCD
 INA219 Zero-Drift, Bidirectional Current/Power Monitor With I2C Interface
INA219 Zero-Drift, Bidirectional Current/Power Monitor With I2C Interface
 SSD1306 OLED driver
SSD1306 OLED driver
 VL53L1X
VL53L1X
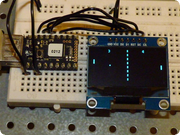 SH1106 OLED driver
SH1106 OLED driver
 PN532 NFC/RFID module
PN532 NFC/RFID module
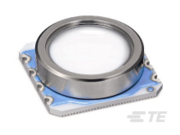 MS5803 Pressure Sensor
MS5803 Pressure Sensor
 VL53L0X
VL53L0X
 Wii Nunchuck
Wii Nunchuck
 MLX90614 Infra Red thermometer
MLX90614 Infra Red thermometer
 MAG3110 3-axis magnetometer
MAG3110 3-axis magnetometer
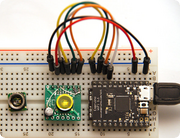 HP03S pressure sensor module
HP03S pressure sensor module
 SSD1327 OLED driver
SSD1327 OLED driver
 MMC212xMG Dual-axis Magnetic Sensor from MEMSIC used in HDMM01 breakout from Pollin
MMC212xMG Dual-axis Magnetic Sensor from MEMSIC used in HDMM01 breakout from Pollin
 MAX1704x Battery Fuel Gauge
MAX1704x Battery Fuel Gauge
 ADS1x15 programmable gain ADC
ADS1x15 programmable gain ADC
 MCP794xx Battery-Backed I2C Real-Time Clock/Calendar with SRAM, (optional) EEPROM and Protected EEPROM
MCP794xx Battery-Backed I2C Real-Time Clock/Calendar with SRAM, (optional) EEPROM and Protected EEPROM
 SHT4x Temperature and Humidity sensor
SHT4x Temperature and Humidity sensor
 LIS3DH Accelerometer
LIS3DH Accelerometer
 BH1750 I2C Light Sensor
BH1750 I2C Light Sensor
 SHT3C Temperature and Humidity sensor
SHT3C Temperature and Humidity sensor
 Sensirion SHT20, SHT21 & SHT25 Temperature and Relative Humidity Sensor
Sensirion SHT20, SHT21 & SHT25 Temperature and Relative Humidity Sensor
 OPT3001 Light Sensor
OPT3001 Light Sensor
 LPS22HB pressure sensor
LPS22HB pressure sensor
 MAX44009 I2C Ambient Light Sensor
MAX44009 I2C Ambient Light Sensor
 CCS811 Digital Air Quality Sensor
CCS811 Digital Air Quality Sensor
 AT24Cxxx I2C EEPROM and FRAM (incl. M24M02, MB85RCxx, FT24Cxxx, 24LCxxx, CAT24Cxxx, BR24Gxxx)
AT24Cxxx I2C EEPROM and FRAM (incl. M24M02, MB85RCxx, FT24Cxxx, 24LCxxx, CAT24Cxxx, BR24Gxxx)
 BME280 Environment sensor
BME280 Environment sensor
 PCA9685 Port Expander
PCA9685 Port Expander
 IS31FL3731 Charlieplexed LED controller
IS31FL3731 Charlieplexed LED controller
 APDS9960 Light and gesture sensor
APDS9960 Light and gesture sensor
 SH1107 OLED driver
SH1107 OLED driver
 BME680 Environment sensor
BME680 Environment sensor
 MPU9250 accelerometer/gyro/magnetometer
MPU9250 accelerometer/gyro/magnetometer
 LIS2MDL Magnetometer
LIS2MDL Magnetometer
 LSM303DLHC Accelerometer
LSM303DLHC Accelerometer
 TSL2561 Luminosity sensor
TSL2561 Luminosity sensor
 TCS3472x I2C Color Sensor
TCS3472x I2C Color Sensor
 SI7021(-A20) I2C Temperature and Humidity Sensor
SI7021(-A20) I2C Temperature and Humidity Sensor
 LSM6DSL Accelerometer and 3D Gyroscope
LSM6DSL Accelerometer and 3D Gyroscope
 HTU21D Temperature and RH Sensor
HTU21D Temperature and RH Sensor
 BH1745 Digital Color Sensor
BH1745 Digital Color Sensor
 HTS221 humidity and temperature sensor
HTS221 humidity and temperature sensor
 BMP280 Environment sensor
BMP280 Environment sensor
 MPU6050 accelerometer and gyro
MPU6050 accelerometer and gyro
 MPL3115A2 Digital Altitude / Pressure / Temperature Sensor
MPL3115A2 Digital Altitude / Pressure / Temperature Sensor
 MPL115A2, I2C digital barometer and temperature sensor
MPL115A2, I2C digital barometer and temperature sensor
 MCP9808 precision I2C temperature sensor
MCP9808 precision I2C temperature sensor
 MCP4xxx I2C and SPI digital potentiometers
MCP4xxx I2C and SPI digital potentiometers
 MCP23xxx I2C and SPI port expanders
MCP23xxx I2C and SPI port expanders
 LPS25HB pressure sensor
LPS25HB pressure sensor
 Digole LCD driver (monochrome)
Digole LCD driver (monochrome)
 CAP1188 capacitive touch breakout
CAP1188 capacitive touch breakout
 BMP085/BMP180 digital pressure sensor
BMP085/BMP180 digital pressure sensor
This page is auto-generated from GitHub. If you see any mistakes or have suggestions, please let us know.